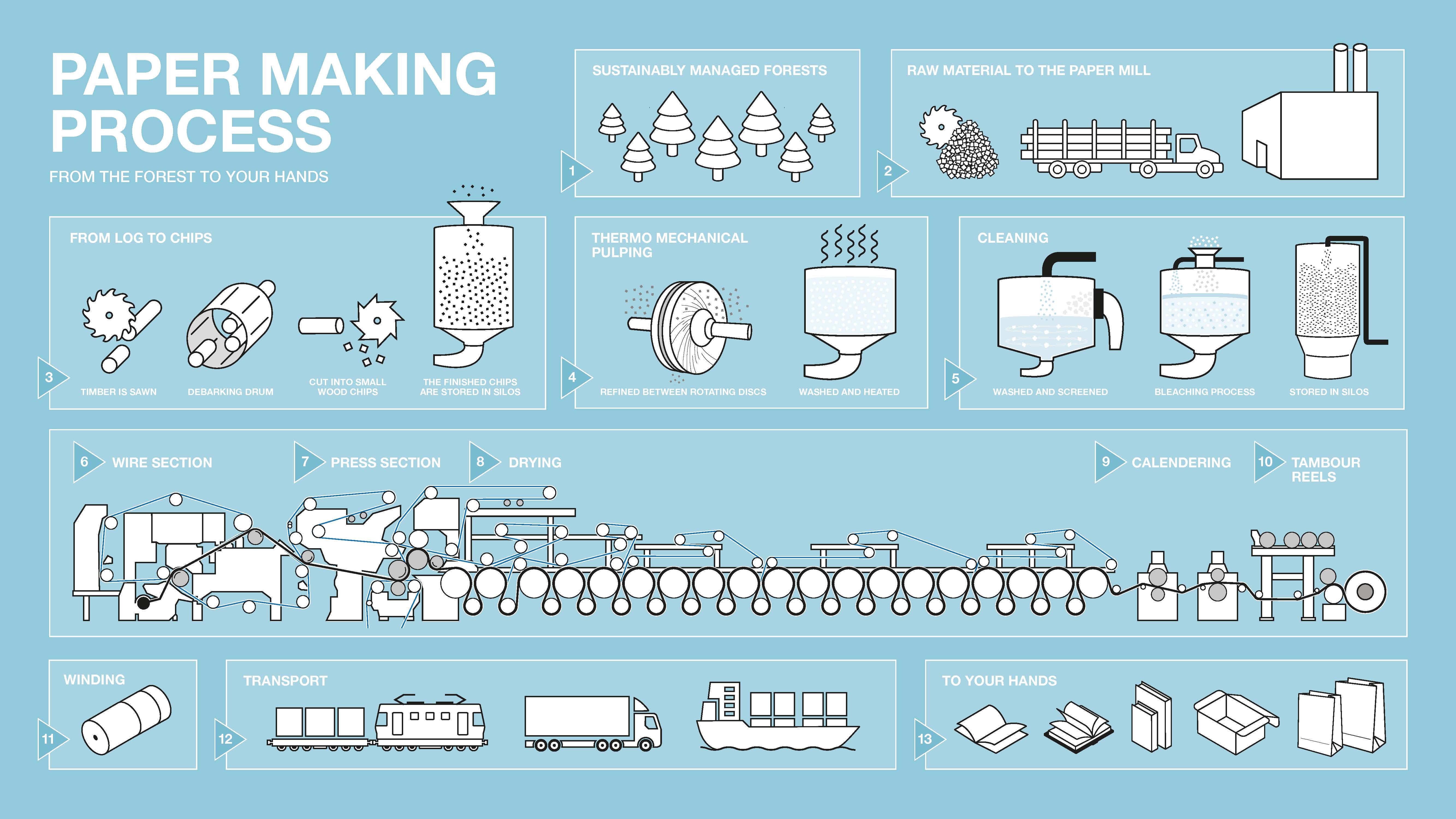
Paper Making Process
Logs to Chips to Pulp to Paper
FROM LOGS TO CHIPS

Step 1: From logs to chips
The pulpwood enters the mill and is washed, debarked, cut and chipped before moving on to the pulping step.
FROM CHIPS TO PULP

Step 2: From chips to pulp
The wood chips are steamed, refined, relaxed and bleached before entering the paper machine.
FROM PULP TO PAPER

Step 3: From pulp to paper
The paper pulp enters the paper machine and exits as a finished sheet of paper after just 15 seconds.
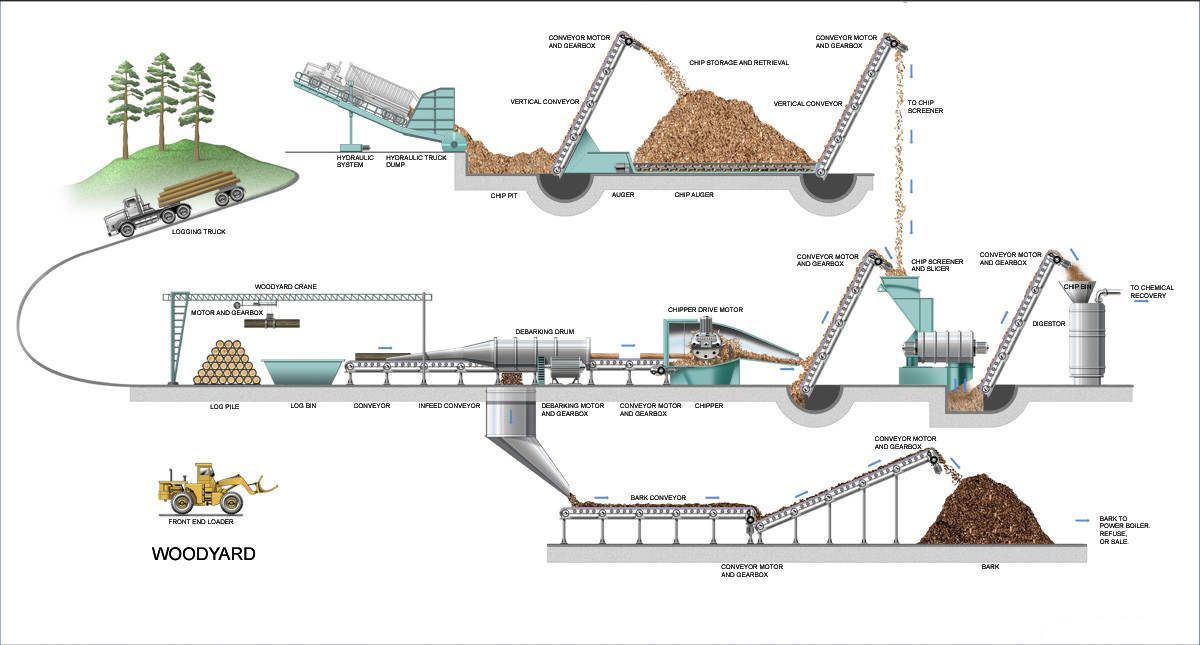
THE PRODUCTION OF WOOD CHIPS
Wood chips are the raw material for producing wood pulp, panelboards and energy. The wood logs need to be converted into small sizes, to facilitate the transportation and further processing.
Depending on the final product, specific demands are requested to the quality of the wood chips. The chip production results depend on type of equipment, layout, operation and maintenance.
Process overview
The place where the chips are produced is called Woodyard. The logs are received by truck, train, boat or water - a river or sea. There is a storage area for logs, to build a buffer for unexpected stops or aging.
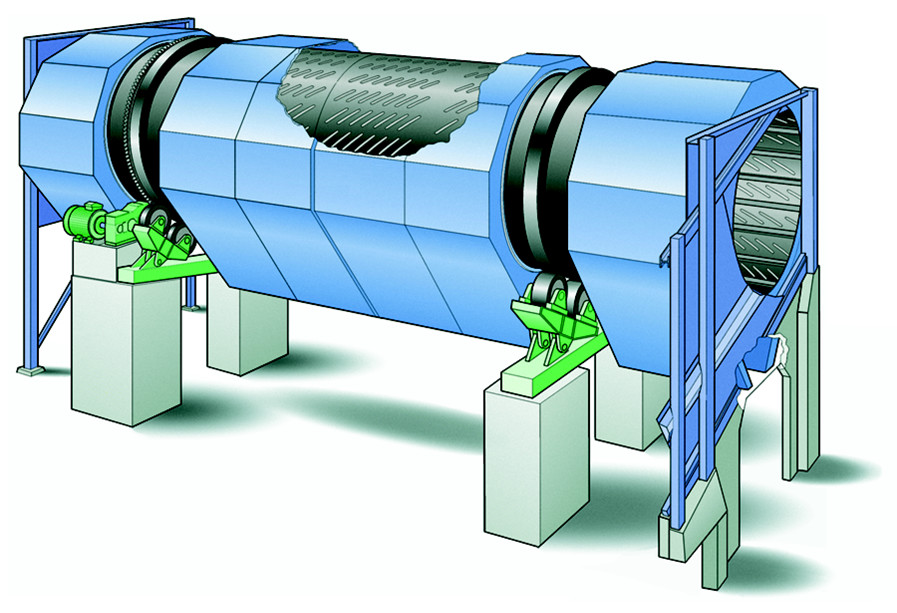
The logs enter into the process through a feeding station. This will take to the next step, that is the debarking drum, if they were not debarked in the forest. The debarking drum will separate the bark with some other impurities, and then send the debarked logs to the chipper.
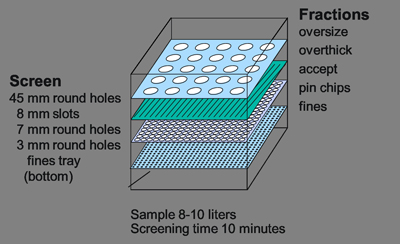
There is a metal detector in the belt conveyor, as well as stone traps. The purpose is to protect the chipper against big and hard contaminants. At the chipper, the wood logs are cut into small sizes. Right after, the chips can be screened or stored. At the screening station, the chips are classified, and only the accepts will be forwarded to the next production area.
Auxiliary systems will process the rejects, residues and secondary flows. They will also provide recycled water to the process, so that the consumption of fresh water is reduced.
Process units
An important but often unknown factor around chip production are the measuring units. The wood logs can me measure in:
- m3 sub - solid cubic meters under bark (logs without bark)
- m3 sob - solid cubic meters over bark (logs with bark)
- Solid cubic meter - 1 solid cubic meter equals to 1,5 piled cubic meter of logs, or 2,7 loose cubic meters of chips.
- Stacked cubic meter
- Piled cubic meter